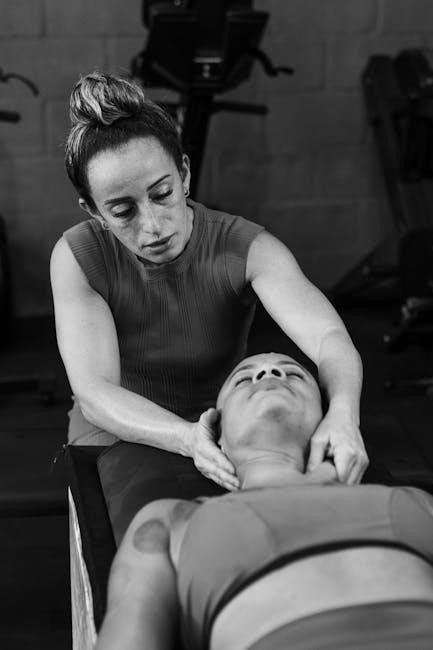
Physical therapy leg strengthening exercises empower individuals to rebuild muscle strength, enhance mobility, and support recovery from injuries or surgeries, focusing on essential lower limb movements.
1.1 Importance of Leg Strength in Physical Therapy
Leg strength is a cornerstone of physical therapy, essential for stability, mobility, and overall functional independence. Strong legs provide the foundation for daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and maintaining balance. Weak leg muscles can lead to injuries, poor posture, and increased risk of falls. Physical therapy focuses on rebuilding and enhancing leg strength to support rehabilitation, improve joint stability, and reduce pain. Strengthening the legs also promotes better circulation, enhances athletic performance, and aids in recovery after surgeries or injuries. Prioritizing leg strength in physical therapy ensures long-term mobility and reduces the likelihood of future musculoskeletal issues.

1.2 Benefits of Leg Strengthening Exercises
Leg strengthening exercises offer numerous benefits, including improved posture, enhanced mobility, and reduced risk of injuries. Stronger legs provide better support for joints, alleviating pain and improving overall stability. These exercises also boost circulation, promoting faster recovery after injuries or surgeries. Strengthening the legs can enhance athletic performance and endurance, making daily activities like walking and climbing stairs easier. Additionally, leg exercises play a crucial role in rehabilitation, helping individuals regain independence and confidence. Regular practice can prevent muscle imbalances and improve balance, reducing the risk of falls. Overall, leg strengthening is essential for maintaining physical health and fostering long-term well-being.
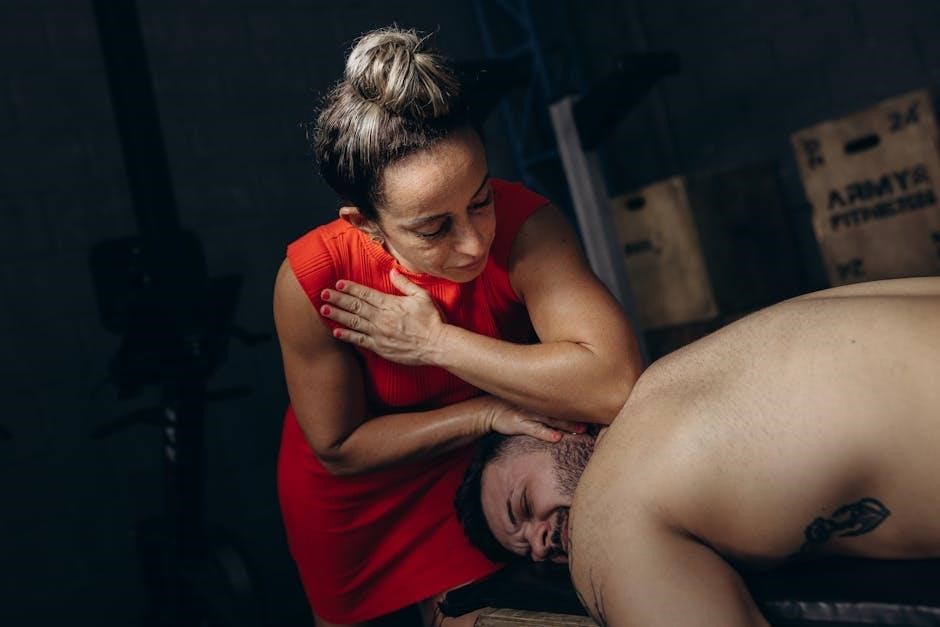

Essential Leg Strengthening Exercises in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy incorporates exercises like seated leg extensions, standing calf raises, and resistance band workouts to enhance leg strength, stability, and functional movement effectively.
2.1 Seated Leg Strengthening Exercises
Seated leg strengthening exercises are a fundamental part of physical therapy, designed to enhance lower limb strength and mobility. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from surgeries or injuries, as they can be performed without placing excessive strain on the joints. Common seated exercises include leg extensions, seated marches, and calf raises, which target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. By incorporating resistance bands or light weights, patients can progressively increase the intensity of their workouts. These exercises not only improve muscle strength but also promote better balance and stability, making daily activities like walking and climbing stairs easier and safer.
2.2 Standing Leg Strengthening Exercises
Standing leg strengthening exercises are essential for improving functional movement and overall lower limb stability. These exercises are ideal for individuals who can bear weight on their legs and are looking to progress from seated exercises. Common standing exercises include bodyweight squats, lunges, calf raises, and single-leg stands. They target multiple muscle groups, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, while enhancing balance and coordination. Resistance bands or light weights can be added to increase intensity. Standing exercises mimic daily activities, making them highly effective for restoring strength and confidence in performing tasks like walking, climbing stairs, and maintaining proper posture.
2.3 Resistance-Based Leg Strengthening Exercises
Resistance-based leg strengthening exercises are highly effective for building muscle endurance and power. They often involve the use of resistance bands, weights, or specialized equipment like leg press machines. These exercises target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, promoting progressive overload to enhance strength. Examples include resisted leg extensions, hamstring curls, and calf raises. Resistance training helps improve joint stability, particularly after injuries or surgeries. It also enhances functional abilities, such as walking and climbing stairs. Physical therapists often tailor resistance programs to meet individual needs, ensuring safe and effective progression. Regular practice of these exercises can significantly accelerate recovery and improve overall lower limb function.
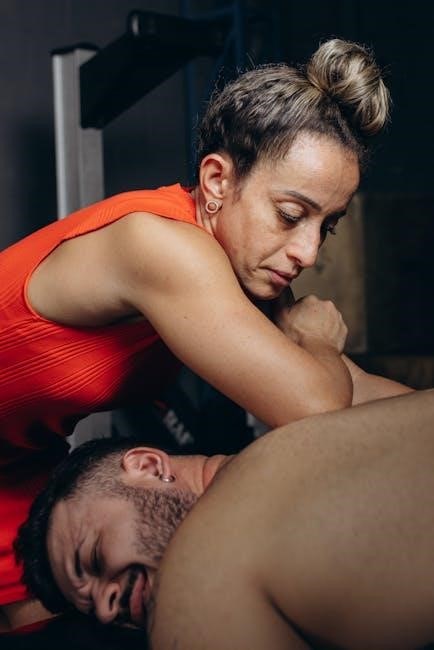

Safety Tips for Performing Leg Strengthening Exercises
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting exercises. Ensure proper form, warm-up, and cool-down to prevent injuries. Tailor routines to individual fitness levels for safe progression.
3.1 Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares the muscles for exercise, reducing injury risk and improving flexibility. Start with 5-10 minutes of light cardio, such as brisk walking or cycling, followed by dynamic stretches like leg swings and lunges. Focus on major muscle groups like quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. After exercising, a cool-down with static stretches helps relieve muscle tension and promotes recovery. Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply to relax. Consistency in these routines enhances overall leg strength and prevents stiffness. Always prioritize these steps to ensure safe and effective physical therapy sessions.
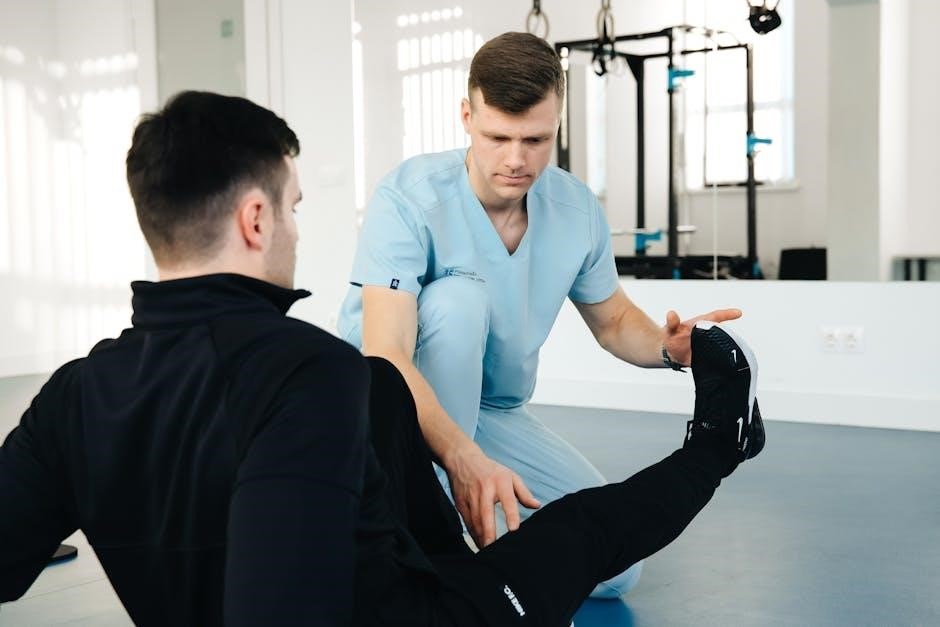

3.2 Proper Form and Technique
Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of leg strengthening exercises and minimizing injury risk. Maintain correct posture during movements, engaging core muscles to stabilize the body. For exercises like squats or lunges, ensure knees track over toes and avoid letting them collapse inward. When performing seated leg extensions, focus on slow, controlled movements to target the quadriceps effectively. Avoid using momentum or sacrificing form for heavier weights, as this can lead to imbalanced strength or muscle strain. Physical therapists often guide patients to ensure technique accuracy, promoting safe and efficient progress in leg strengthening programs.

Progression and Consistency in Leg Strengthening Programs
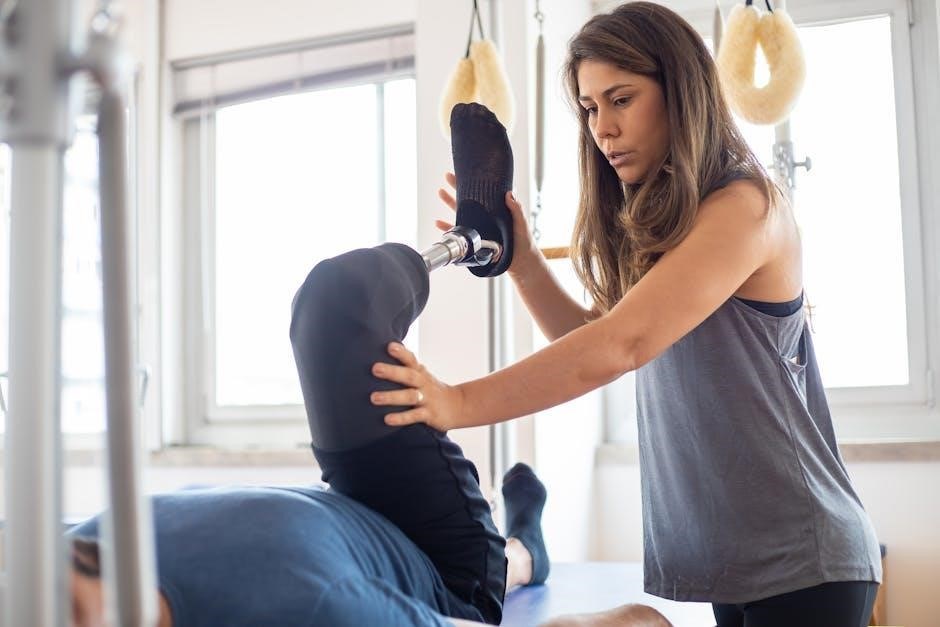

Progression and consistency are vital for effective leg strengthening; Gradually increase exercise intensity and repetition to avoid plateaus, ensuring steady muscle growth and recovery under professional guidance.
4.1 Gradually Increasing Exercise Intensity
Gradually increasing exercise intensity is crucial for effective leg strengthening. Start with low-resistance movements, such as seated leg extensions or resistance band exercises, and slowly progress to higher loads. This approach prevents injury and promotes steady muscle recovery. Over time, increase repetitions, sets, or resistance to challenge muscles further. For example, introduce weighted ankle cuffs or advance to standing exercises with balance challenges. Monitoring progress and adjusting intensity ensures continuous improvement without overexertion. Consistency and patience are key, as gradual progression fosters sustainable strength gains and supports long-term mobility. Always consult a physical therapist to tailor intensity adjustments to individual needs and goals.
4.2 Role of Consistency in Recovery
Consistency is vital for effective recovery in leg strengthening programs. Regular performance of prescribed exercises ensures steady progress, helping muscles rebuild strength and improve mobility. Irregular efforts often lead to slower recovery and may hinder overall improvement. A structured routine, maintained over time, reinforces muscle memory and promotes sustainable gains. Even small, daily commitments can yield significant long-term benefits. Patients are encouraged to adhere to their physical therapy plans, as consistency directly impacts the effectiveness of rehabilitation. This dedication supports the body’s natural healing process and helps achieve the goals set by healthcare providers for optimal recovery and functional independence.
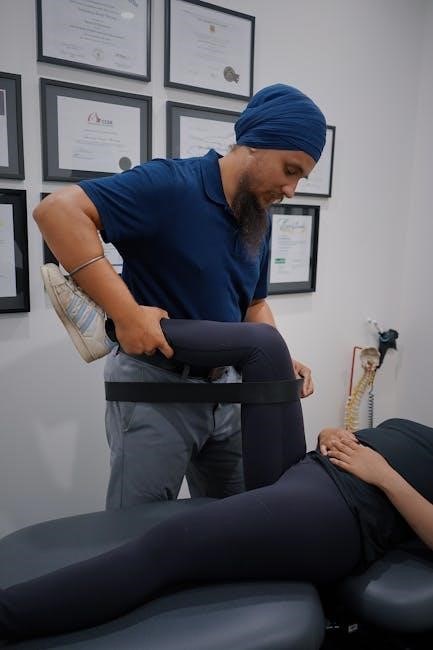
Specific Muscle Groups Targeted in Leg Strengthening
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening key leg muscles, including quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, and glutes, to enhance mobility and prevent injuries, improving overall lower limb function and stability.

5.1 Quadriceps Strengthening Exercises
Quadriceps strengthening exercises are crucial for improving knee stability and overall leg function. Common exercises include straight leg raises, step-ups, and seated leg extensions. These exercises target the quadriceps muscles, essential for activities like walking, climbing stairs, and maintaining balance. Straight leg raises, performed while lying or sitting, help activate the quadriceps without putting strain on the knee joint. Step-ups strengthen the quadriceps and improve functional mobility. Seated leg extensions, often done with resistance bands or weights, enhance muscle endurance and strength. Consistent practice of these exercises can prevent injuries and support recovery after surgeries or injuries affecting the knee and surrounding areas.
5.2 Hamstring Strengthening Exercises
Hamstring strengthening exercises are vital for improving posterior thigh muscle function, essential for activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs. Common exercises include seated leg curls, glute-ham raises, and bridges. Seated leg curls target the hamstrings directly, promoting muscle activation and strength. Glute-ham raises combine glute and hamstring engagement, enhancing overall lower limb stability. Bridges, performed lying down, strengthen hamstrings while engaging the core. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from knee injuries or surgeries. Regular practice improves knee stability, reduces injury risk, and enhances functional mobility. Strengthening hamstrings also supports proper posture and movement efficiency, making them a cornerstone of leg strengthening programs.
5.3 Calf Strengthening Exercises
Calf strengthening exercises are essential for enhancing lower leg function and mobility. Calf raises, both seated and standing, are fundamental exercises that target the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. These movements improve ankle stability, balance, and overall lower limb strength. Seated calf raises allow for controlled resistance, while standing calf raises incorporate body weight for natural strengthening. Incorporating calf stretches and heel raises on a step can further enhance flexibility and muscle endurance. Strong calves are crucial for activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs. Regular practice helps prevent injuries, supports post-surgery recovery, and improves mobility. Consistency in these exercises ensures long-term benefits for leg health and functional independence.
5.4 Glute Strengthening Exercises
Glute strengthening exercises are vital for improving lower limb stability, posture, and overall mobility. Exercises like bridges, side-lying leg lifts, and bird dogs target the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus muscles. These movements help restore proper hip function, reduce injury risk, and enhance athletic performance. Bridging strengthens the glutes while engaging the core, while side-lying leg lifts focus on hip abduction. Bird dogs improve balance and coordination by engaging the glutes and lower back. Strong glutes are essential for activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs. Incorporating these exercises into a physical therapy routine can help address imbalances, alleviate lower back pain, and promote long-term functional independence.
