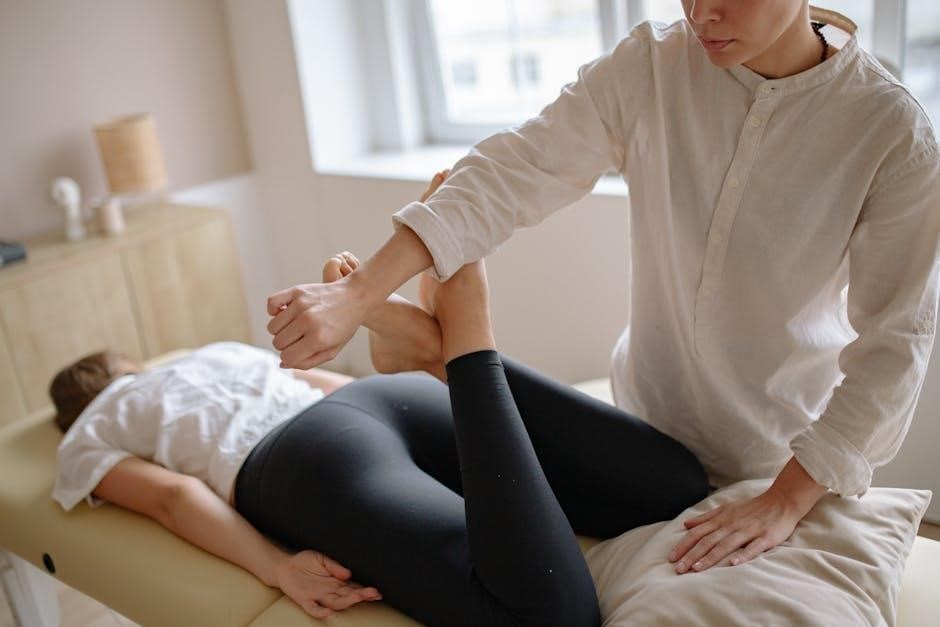
Manual therapy techniques are a collection of hands-on methods used to enhance movement, relieve pain, and improve bodily function. They are applied by skilled practitioners to address various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions, promoting recovery and restoring mobility in patients. These techniques form the foundation of physical therapy and rehabilitation programs, offering personalized approaches to achieve optimal wellness and functional independence.
Definition and Purpose of Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is a hands-on approach using skilled techniques to improve movement, reduce pain, and restore function. Its purpose is to address musculoskeletal and neurological conditions, enhancing recovery and mobility. Practitioners use methods like joint mobilization and soft tissue work to promote healing, alleviate stiffness, and optimize physical performance, tailored to individual patient needs.
Historical Development and Evolution
Manual therapy traces its roots to ancient practices, with evidence of joint manipulation in early civilizations. Over centuries, techniques evolved, influenced by medical advancements. The 20th century saw formalization of methods like osteopathy and chiropractic care. Today, manual therapy is a cornerstone of physical therapy, integrating evidence-based practices for effective treatment of musculoskeletal and neurological disorders.
Applications in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Manual therapy techniques are widely used in physical therapy to address chronic pain, post-surgical recovery, and mobility issues. They enhance joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, and improve circulation. Common applications include treating musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, and postoperative rehabilitation. These techniques complement exercises and other therapies, fostering faster recovery and improved functional outcomes for patients.
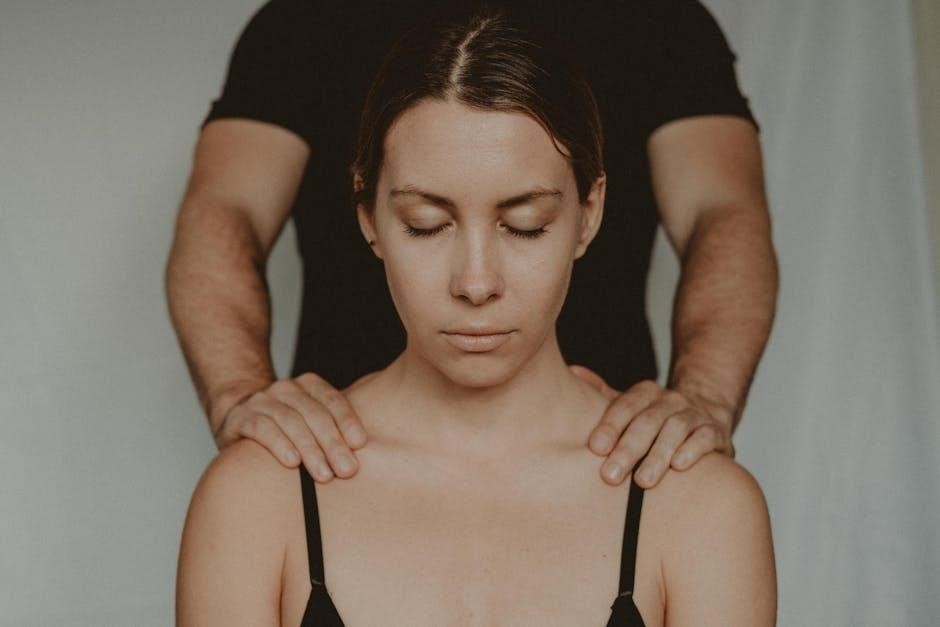

Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization involves skilled passive movements applied to joint complexes to enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness, aiding pain relief and restoring functional movement.
Types of Joint Mobilisation Techniques
Joint mobilisation techniques include passive movements, oscillations, and sustained stretches applied to joints. They are categorized into grades, ranging from light, pain-free movements to deeper, more forceful manipulations. These techniques aim to improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and restore normal movement patterns, addressing various musculoskeletal conditions effectively through targeted, skilled applications by therapists.
Benefits and Indications for Joint Mobilisation
Joint mobilisation enhances joint mobility, reduces pain, and improves functional movement. It is effective for conditions like arthritis, post-surgical stiffness, and sports injuries. Skilled therapists use these techniques to restore range of motion, alleviate stiffness, and promote recovery in patients with musculoskeletal or neurological impairments, aiding in faster rehabilitation and improved quality of life.
Contraindications and Safety Considerations
Joint mobilisation is contraindicated in cases of acute fractures, severe inflammation, or joint instability. Conditions like osteoporosis, recent surgeries, or ligamentous ruptures require caution; Proper diagnosis and skilled application are essential to avoid adverse effects. Patient-specific factors, such as acute injuries or systemic diseases, must be considered to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Soft Tissue Mobilization (STM)
Soft Tissue Mobilization (STM) involves targeted pressure and stretching to relax rigid muscles, release tension, and reduce pain and inflammation. It enhances fluid movement and promotes healing in affected areas, improving overall mobility and comfort for patients with musculoskeletal conditions.
Techniques and Methods in Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft Tissue Mobilization (STM) employs techniques like deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy to target muscle and connective tissue. Practitioners use hands-on methods or tools such as foam rollers to apply pressure, promoting relaxation, improving circulation, and reducing adhesions. These methods enhance flexibility and alleviate pain, addressing both acute and chronic conditions effectively.
Therapeutic Effects on Muscles and Connective Tissue
Soft Tissue Mobilization enhances blood flow, reduces muscle spasms, and breaks down adhesions in connective tissue. It improves flexibility, relieves tension, and promotes healing by releasing restricted areas. These effects reduce pain, restore normal tissue function, and support overall recovery, making it a valuable approach for addressing musculoskeletal and inflammatory conditions effectively.
Myofascial Release
Myofascial Release is a technique using gentle, sustained pressure to relieve fascial tension, enhancing mobility and reducing pain. It targets the connective tissue to improve movement and comfort.
Principles and Mechanisms of Myofascial Release
Myofascial Release involves applying gentle, sustained pressure to fascia to relieve tension and restrictions. It works by enhancing fascial glide, improving circulation, and reducing inflammation. The technique targets connective tissue dysfunction, promoting relaxation and restoring normal movement patterns. By addressing fascial tightness, it alleviates pain, improves flexibility, and supports overall musculoskeletal health and function.
Common Techniques and Tools Used
Common techniques include cross-friction massage, deep tissue work, and myofascial stretching. Tools like foam rollers, soft tissue mobilizers, and hands-on methods are frequently used. These approaches target fascial restrictions, promoting relaxation and improving mobility. They are often combined with patient movement to enhance outcomes and address specific tissue dysfunctions effectively.
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET)
Muscle Energy Techniques involve patient-generated muscle contractions to improve joint mobility and function. They are widely used in rehabilitation, particularly for spinal and extremity conditions, enhancing movement efficiency.
Definition and Application of Muscle Energy Techniques
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET) are manual therapy methods using voluntary muscle contractions to improve joint mobility and function. Applied by trained therapists, MET addresses spinal and extremity dysfunctions, enhancing movement and reducing stiffness. It’s particularly effective for conditions like sciatica and frozen shoulder, promoting neuromuscular control and pain-free motion through targeted, patient-activated movements.
Advantages and Clinical Applications
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET) offer non-invasive, patient-activated approaches to improve joint mobility and neuromuscular control. Clinically, MET is effective for treating sports injuries, chronic pain, and post-surgical rehabilitation. Its adaptability makes it suitable for diverse conditions, enhancing functional recovery and reducing stiffness, while promoting pain-free movement and restoring optimal musculoskeletal function in patients.
Strain Counterstrain
Strain Counterstrain is a gentle, non-invasive manual therapy technique that targets muscle spasms and joint dysfunction. It involves passive positioning to relieve pain and improve mobility effectively.
Concept and Methodology of Strain Counterstrain
Strain Counterstrain is a manual therapy approach that uses passive positioning to alleviate muscle spasms and joint dysfunction. The technique involves identifying tender points and gently moving the affected joint into a position of comfort, reducing pain and improving mobility. It focuses on addressing neuromuscular reflexes to restore normal joint and muscle function effectively.
Efficacy in Pain Relief and Functional Improvement
Strain Counterstrain is highly effective in reducing pain and improving functional mobility. By addressing muscle spasms and joint dysfunction, it enhances movement and reduces discomfort. This technique is particularly beneficial for acute and chronic pain, promoting faster recovery and improving patients’ ability to perform daily activities with greater ease and reduced inflammation.
Neural Tissue Tension Techniques
Neural Tissue Tension Techniques target nerve-related discomfort, enhancing mobility and reducing pain through specialized exercises and manual interventions, often used in conditions like sciatica or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Understanding Neural Tissue Tension and Its Impact
Neural tissue tension occurs when nerves experience abnormal stress or restriction, often due to inflammation, scar tissue, or poor posture. This can impair nerve mobility, leading to pain, limited range of motion, and discomfort in affected areas. Addressing neural tension is crucial for restoring normal nerve function and improving overall musculoskeletal health, reducing pain and enhancing mobility.
Techniques to Alleviate Neural Tension
Neural tissue tension techniques involve gentle, targeted manipulations to restore nerve mobility and reduce discomfort. Methods include nerve sliding, tensioning, and mobilization, which enhance nerve glide and reduce adhesions. These techniques are applied with precision to improve circulation, alleviate pain, and restore normal neural function, promoting overall musculoskeletal balance and patient comfort effectively.

Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
PNF involves controlled muscle contractions and stretching to enhance flexibility, strength, and coordination. It improves neuromuscular communication, making it highly effective in rehabilitation and physical therapy programs.
Principles of PNF and Its Role in Rehabilitation
PNF is based on diagonal patterns of movement, resistance, and neuromuscular control. It enhances motor learning, joint stability, and functional movement by stimulating proprioceptors. This technique is widely used in rehabilitation to restore lost or impaired motor skills, improve coordination, and strengthen muscles, making it a cornerstone of physical therapy for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries.
Techniques and Exercises in PNF
PNF incorporates resisted exercises, manual resistance, and stretching to enhance strength, flexibility, and coordination. Techniques include resisted leg and arm movements, diagonal patterns, and functional activities. These exercises are tailored to individual needs, promoting neuromuscular activation and motor control. They are often performed with a therapist’s assistance or specialized equipment to maximize therapeutic outcomes and patient engagement.
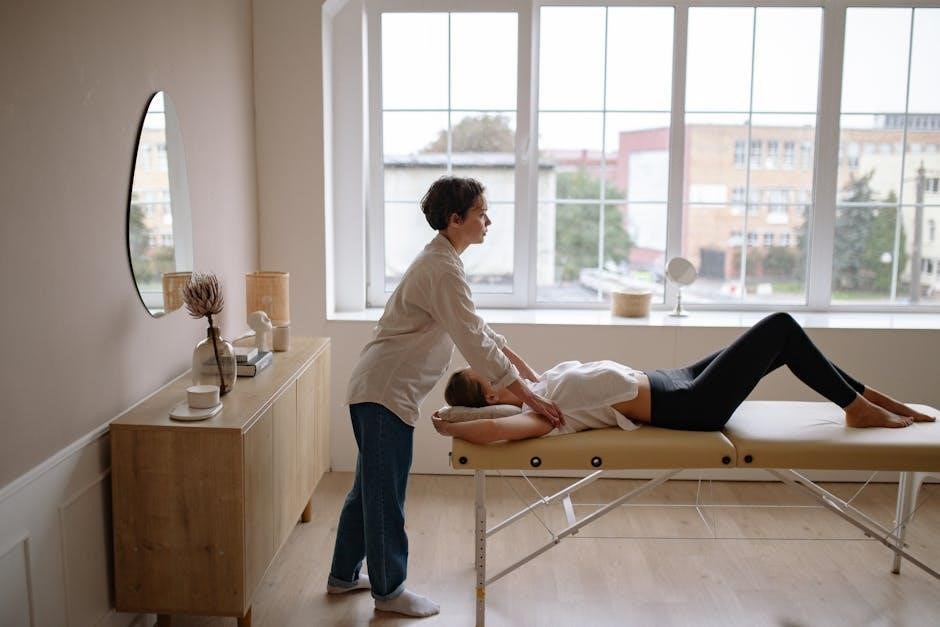

Joint Manipulation
Joint manipulation involves targeted joint movements applied by skilled therapists to restore mobility and relieve pain, enhancing functional movement and overall joint health effectively.
Types of Joint Manipulation Techniques
Joint manipulation techniques include high-velocity low-amplitude thrusts, joint distraction, mobilization with movement, and soft tissue techniques. These methods target specific joints to improve mobility and reduce pain, often used in chiropractic and physical therapy settings to address stiffness and dysfunction, enhancing overall joint function and patient comfort effectively.
Benefits and Risks of Joint Manipulation
Joint manipulation offers immediate relief from stiffness and pain, enhancing joint mobility and improving functional movement. However, risks include temporary discomfort, muscle soreness, or rare complications like injury to ligaments or discs. Skilled practitioners minimize risks, ensuring safe application tailored to individual needs for optimal therapeutic outcomes and improved patient well-being.
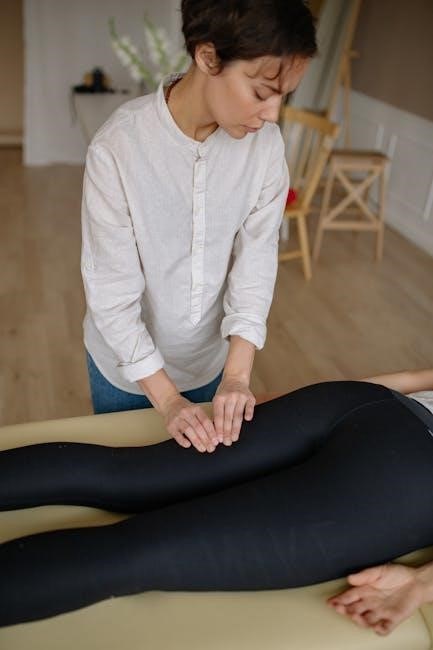

Therapeutic Stretching
Therapeutic stretching is a manual therapy technique aimed at improving flexibility, mobility, and reducing muscle tension. It helps manage conditions limiting movement, enhancing range of motion.
Methods and Benefits of Therapeutic Stretching
Therapeutic stretching involves techniques like static, dynamic, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching. These methods enhance flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and improve joint mobility. Benefits include pain relief, injury prevention, and improved circulation. Regular stretching promotes relaxation, reduces stiffness, and enhances overall physical function, making it a cornerstone of rehabilitation and wellness programs.
Integration with Other Manual Therapy Techniques
Therapeutic stretching is often combined with joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and myofascial release to enhance treatment outcomes. This integrated approach promotes improved mobility, reduces muscle tension, and accelerates healing. By incorporating stretching with other manual techniques, practitioners can address multiple aspects of dysfunction, creating a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan for optimal patient care.
Manual therapy techniques are effective for pain relief, restoring movement, and improving function. Their integration empowers patients, enhancing recovery and promoting long-term wellness through personalized care approaches;
Manual therapy encompasses diverse techniques like joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, and muscle energy techniques. These methods enhance movement, reduce pain, and restore function. Each approach targets specific tissues, promoting recovery and improving overall well-being. Skilled practitioners tailor these techniques to individual needs, fostering optimal outcomes and empowering patients to achieve functional independence and improved quality of life.
Future Trends and Developments in Manual Therapy
Future trends in manual therapy include the integration of advanced technologies like AI and VR for personalized treatment. Telehealth platforms are expanding access to manual therapy, while research focuses on optimizing techniques for chronic pain and neurological conditions. Interdisciplinary collaboration and evidence-based practices are expected to shape the evolution of manual therapy, enhancing patient outcomes.
